Chapter 5
# Market Power
# Imperfect Markets
Imperfect Markets Imperfect markets are not in the course outline
The model of demand and supply applies to a competitive market.
- This is characterised by a large number of small firms, free entry and exit and very little product differentiation.
- When one or more of these conditions are not met, the the market is ‘imperfect’
# Imperfect markets exists when:
- Relatively small number of firms
- Firms have market power
- Firms use product differentiation
- barriers to entry are used to restrict competition
# Examples
- Monopoly
- Is a market with just one firm
- E.g. Synergy, Australia Post
- Oligopoly
- Is a market with a few large dominant firms
- E.g. Coles and Woolworths dominate the grocery market in Australia
In an imperfect market, firms are said to have market or ‘monopoly’ power which means that they can set the price.
Higher prices in imperfect markets due to less competition.
# Barriers to Enter
- Are an important feature of imperfect markets
Definition A barrier to entry is anything that restricts or blocks the entry of new firms into an industry or market. They may include government regulation, and patents, technology barriers, start-up costs and licensing requirements.
# Examples
Controlling a scarce resource
- If a mining company pegged the only diamond mine in the country, it would have sole rights to mine the gems
A Government licence granting a legal monopoly
- E.g. Australia Post
A technological advantage
- E.g. Microsoft has considerable market power because it supplies the operating system used in most computers
A patent on an invention gives protection from competition
- Up to 17 years in Australia
# Imperfect Market Exploitation
- Imperfect markets $\rightarrow$ Firms use market power to ’exploit’ the market.
- A firm has market power if it can affect the market price by varying its output.
- Firms with market power will try to maximise profit.
- Private interest $\rightarrow$ not necessarily align with society
# Anti-Competitive Behaviour
- Firms with market power $\rightarrow$ incentive to reduce competition
- Either reducing price competition or by reducing the number of firms competing in the market
Anti-Competitive Behaviour Refers to any agreements or arrangements between firms that seek to restrain competition and thereby remove the automatic regulation that competitive markets achieve
# Externalities
Externalities The side effects of economic activity are referred to as externalities.
# Negative Externalities
Examples:
- Smog from driving cars
- Lawn mowers create noise pollution
- Use of fossil fuels contribute to global warming
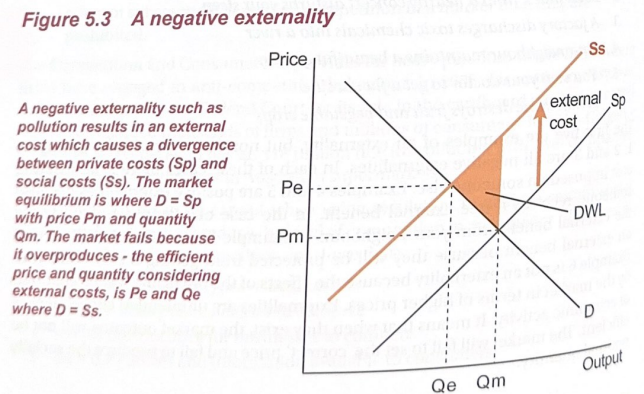
Negative Externalities When economic actions from either production or consumption create an external cost, it is referred to as a negative externality.
Pollution is a classic example of a negative externality.
- A factory that emits pollutants into the atmosphere is likely to impose an external cost on those people who are affected by the pollutants
- Firms pollute the environment as it is free (no one owns it)
- If the firm was forced to install air filters to eliminate the pollutants, then there would be no external cost and there would be no market failure
Social cost is equal to private costs plus external cost
# Positive Externalities
Positive Externalities Positive externalities create an external benefit for third parties
Social benefit is equal to private benefits plus external benefits
# Government Policy and Externalities
When externalities exist, the market outcome will not be efficient - the optimal quantity will not be produced and the price charged may not reflect the true value of the resources used in production.
Governments can use market based policies to correct for externalities.
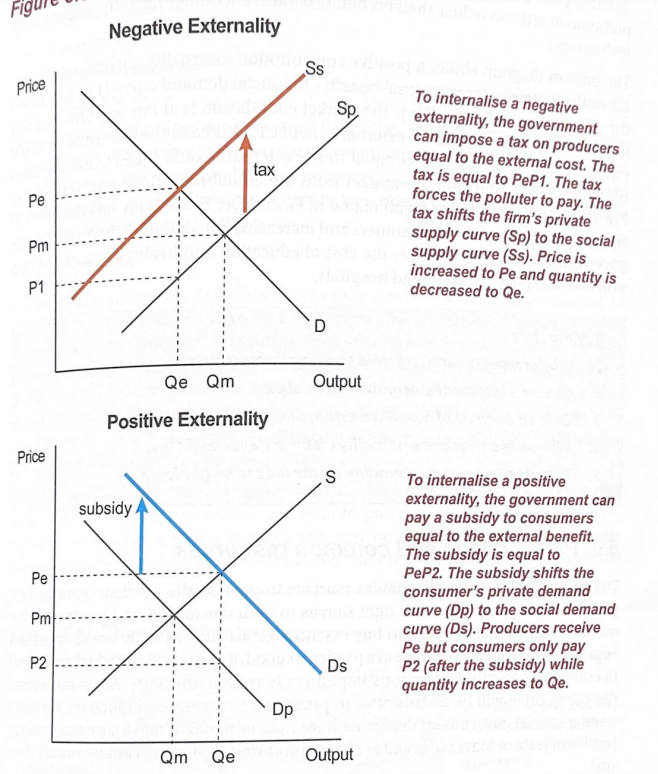
Negative externality $\rightarrow$ tax should be placed on the producer to reduce output Positive externality $\rightarrow$ subsidy should be used to increase output
# Types of Goods
# Classification of Goods
# Rival
- Does the consumption by one party reduce the supply available for another?
# Excludable
- Is it possible to exclude a non-payer from the good or service
# Private Goods
Rival
- Your consumption of the good or service means another party cannot consume it Excludable
- There are requirements to be met before being able to access the good or service
# Club Goods
Non-Rival
- Your consumption of the good or service does not prevent another party from consuming it Excludable
- There are requirements to be met before being able to access the good or service
# Common Property Resources
Rival
- Your consumption of the good or service means another party cannot consume it Non-Excludable
- There are no requirements to be met before being able to access the good or service
# Public Goods
Non-Rival
- Your consumption of the good or service does not prevent another party from consuming it Non-Excludable
- There are no requirements to be met before being able to access the good or service
| Rival | Non-Rival | |
|---|---|---|
| Excludable | Private Good | Club Good |
| Non-Excludable | Common Resource | Public Good |
# Market Failure
# Tragedy of the Commons - Common Property Resources
- Refers to the over-consumption of common property resources
- Occurs as the resource is readily available and there are no restrictions on consumption
- However, once consumed the resource is not available to any other party.
# Free Rider Effect - Public Goods
- Free riders enjoy the benefits of the consumption of a resource without paying for the cost of provision
- This can lead to over-consumption and rapid damage of a public resource
# Policy Options to Address the Market Failure
# Common Property Goods
- Enforce restrictions on consumption - eg fishing limits
# Public Goods
- Create ownership of the resource - eg fines, fees
# Merit Goods and Demerit Goods
Merit goods
- Goods that are produced that have large external benefits for society
- Goods that will be underprovided in the economy if the product is left in the market
Demerit goods
- Goods that are produced that have large external costs for society
- Goods that will be overprovided if left in the market
- Are private goods as they are both rivalry and exclusive