Intro to Macroeconomics
# Intro to Macroeconomics
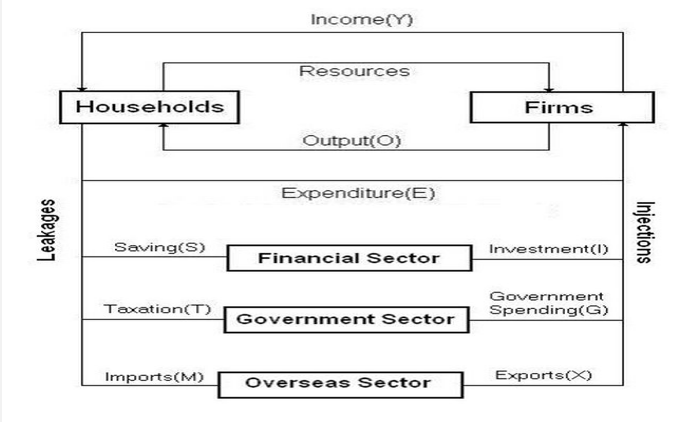
# Circular Flow of Income
Definition A Macroeconomic model that describes the flows of resources, goods and service, income and expenditure between different parts of the economy.
# Includes
- Firms
- Households
- Government
- Financial Sector
- Overseas
# Diagram of the CFI
# Households and Firms
# Assumptions
- Households own all the resources and are buyers
- Firms are employers and produce goods and services
- Factor market
- Product market
- The two markets are interdepended
# Injections and Leakages
# Injections
Definition Inflow of money into the circular flow of income
- Investment (I)
- Government Expenditure (G)
- Exports (X)
# Leakages
Definition Outflow of money from the circular flow of income
- Savings (S)
- Taxation (T)
- Imports (M)
# Equilibrium
- An economy is in equilibrium when the sum of all leakages = the sum of all injections
- Occurs when S+T+M = I+G+X
- Sum of all output (O) = Sum of all Expenditure (E) = Sum of all income (Y)
- All the income from households equals the expenditure on goods and services which equals the total production in the economy
# Changes to Equilibrium
# S>I
- Flow of Y must contract
- Total spending is less than output
- Inventories increases due to less expenditure
- Firms decrease production
- Households receives less income TBF
# Aggregate Expenditure
# Measuring Economic Performance
# GDP
- Expenditure approach
- Addition of all final expenditures within a country given a period of time
- National income approach
- Addition of al income earned from factors of production that produce goods and services given a period of time
- Output approach
- Addition of all value of goods and services produced in a country given a period of time
# Aggregate Expenditure
Definition Total amount that firms, households and government plan to spend on final goods and services at each level of income
- Calculated as AE = C + I + G + (X-M)
# Consumption
# Components
Households expenditure goods and services:
- Durables: >3 years
- Non-durables: <3 years
- Services
- Something else
# Factors Affecting Consumption
- Disposable income: More income = more spending
- Interest rates: High interest rates = more saving
- Availability of credit: More loans = more spending
- Stock of personal wealth: More wealth = more spending
- Expectations: Expecting economy downturn = more saving
- Government policies: Higher tax = less spending
# Private Investment
Definition Expenditure on producer or capital goods that are used to produce final goods and services in the future
# Investment by private firms
- Fixed investment (usually on capital goods)
- Residential fixed investment (private expenditure on new housing)
- Changes in business inventories (stocks of goods that have been produced but not sold)
# Factors Affecting Investment Expenditure
- Rate of interest (nominal vs real rates): Higher interest rates = less spending
- Business expectations
- Level of past profits (profitability)
- Government policies
# Government Expenditure
- All federal, state, local government expenditure
- 2 parts:
- G1: Current government expenditure on day to day functions
- G2: Government expenditure used for future needs
# Factors Affecting Government Expenditure
- Government policy objectives
- Current economic climate
# Net Exports
- Value of exports minus value of imports
# Factors Affecting Net Exports
- Exchange rates: $AUD increases = Imports decreases and exports increase
- Domestic and overseas economic activity: Aus doing well = Imports increase, overseas doing well = Exports increase
- Tariffs/Quotas: Higher tariffs = decrease